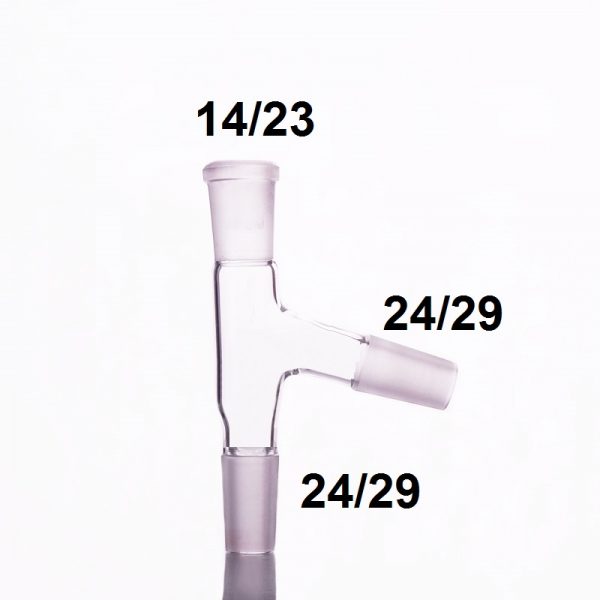
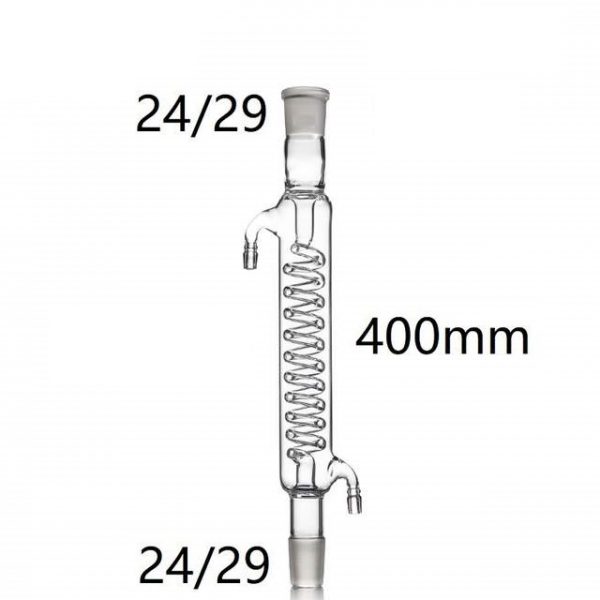
Rotary Evaporator 0.5-2L
Rotary Evaporator 0.5-2L
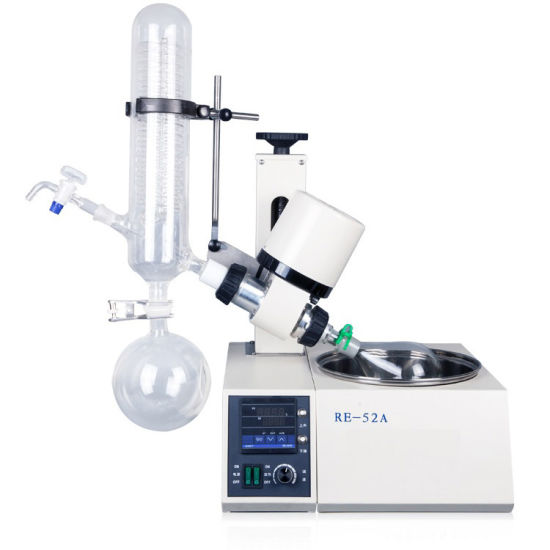
RE-52A rotary evaporator is developed by applying the principle of constant temperature heating and thin film evaporation under vacuum and negative pressure. The instrument is controlled by imported high-grade frequency converter. Stepless speed regulation makes the glass rotary bottle rotate at constant speed. Material forms a large area of uniform film on the wall of the bottle. Then the rotating bottle is heated uniformly by a controllable constant temperature water bath pot. Under the condition of vacuum extraction, the solvent vapor is evaporated at high speed. The solvent vapor is cooled by a high-efficiency glass double condenser and recycled into the collection bottle. The instrument is also equipped with feeding interface and feeding mechanism to facilitate automatic and continuous operation in the evaporation process.
Specifications
| Model | RE-52A |
| Glass Material | GG-17 |
| Bracket Material | Spraying anticorrosion |
| Material of pot shell | Spraying anticorrosion 250*365*150mm |
| Material of Pan gallbladder | Stainless steel 240*120mm |
| Rotating bottle volume | 1L 24#Standard mouth |
| Collect bottle volume | 0.5L 24#Standard mouth |
| vacuum degree | 0.098Mpa |
| Rotating power | 30W |
| Rotating speed | 0-120rpm |
| heating power | 1KW |
| Temperature control range of bathtub | 0-99℃ |
| control accuracy | ±1℃ |
| Lifting trip | 120mm |
| Voltage/frequency (V/Hz) | 220V/50Hz |
| Shape size (mm) | 700*440*1005 |
| Packing dimensions (mm) | 590*460*460 0.12square |
| Packing weight (KG) | 21 |
| Speed regulation mode | e-cvt |
| Temperature display mode | CU50 Type D Sensor Digital Display |
| temperature control | Intelligent Temperature Control |
| Sealing method | Tetrafluoro Component Sealing |
| condenser | Vertical condenser 85*460mm 29# Standard mouth |
| Lifting mode | Manual lift |
| Continuous Feeds | 19# Label feeding valve |


 Labdisc
Labdisc Botzees
Botzees Edison
Edison Telepresence Robot
Telepresence Robot DOBOT
DOBOT Keyestudio
Keyestudio Fischertechnik
Fischertechnik