Skin Block Model
The skin is the largest human organ, both in terms of its weight and the body surface it covers. It is anatomically distinguished in 3 basic cell layers, the epidermis, the dermis and the subcutaneous or adipose tissue, from the outside to the inside. Each layer has a different cellular composition and therefore a different structure and function. The skin of an adult has an area of about 160 m2 and constitutes 8% of his body weight.
Skin surface
On the surface of the skin we find lipids, hairs, fine wrinkles and other elements such as freckles, moles, pores.
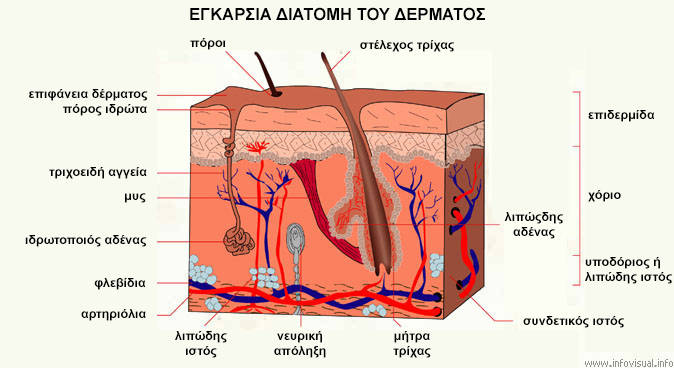
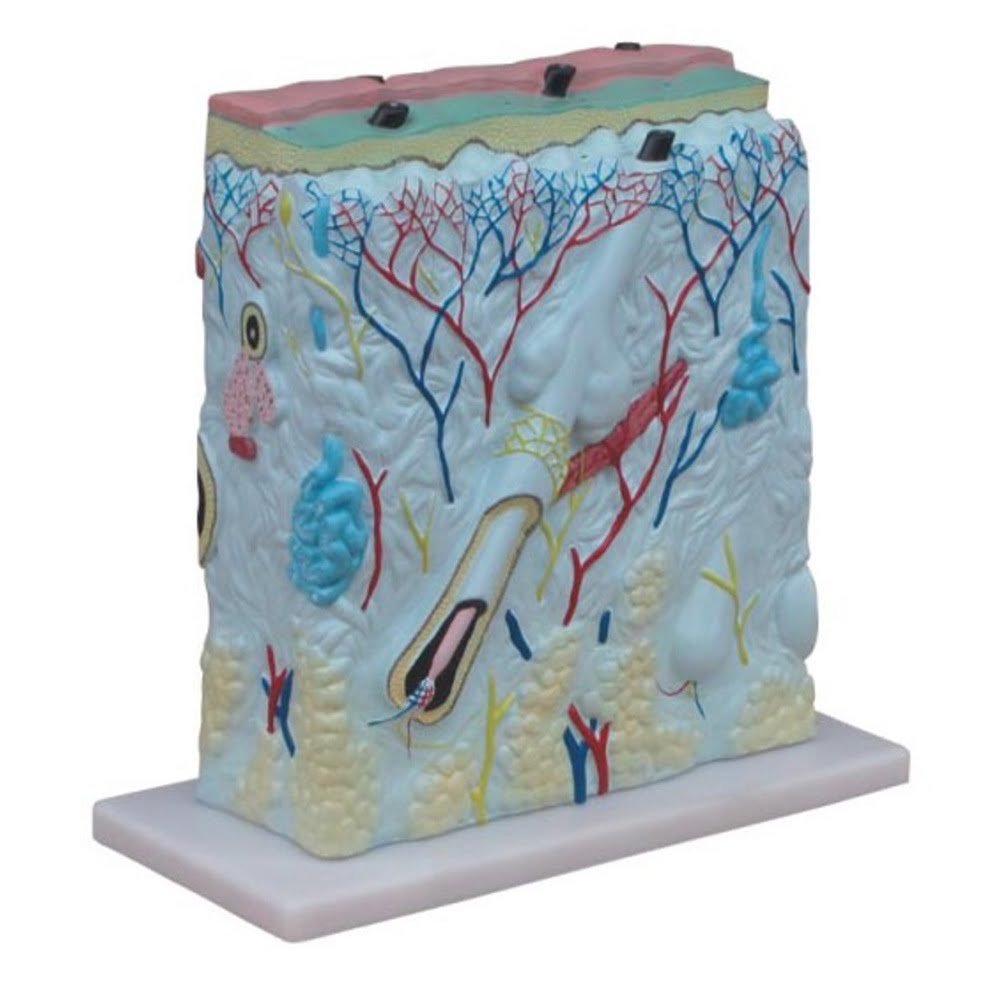
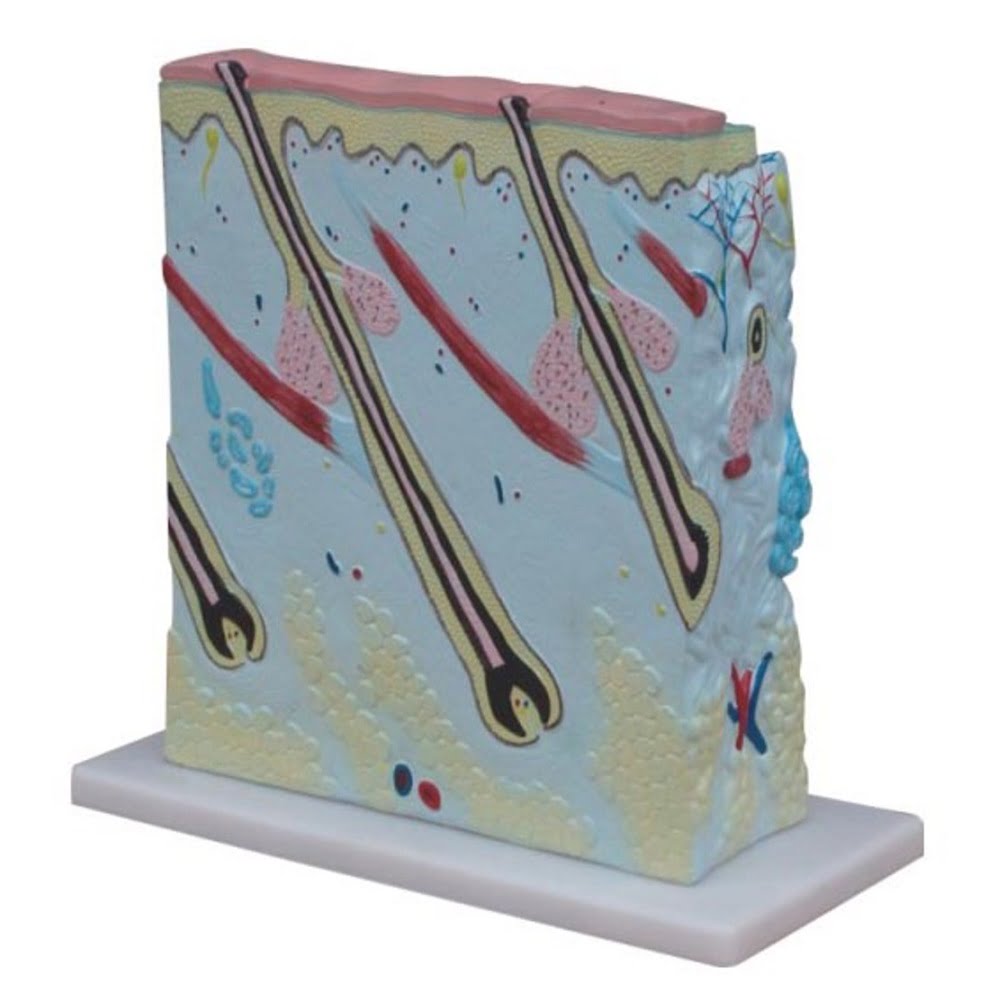
Skin Block Model
CELLS
The cells that make up skin tissue are keratinocytes, fibroblasts, fat cells, melanocytes and erythrocytes. We find them in different layers and they have different structures and functions.
Keratinocytes: They produce a fibrous protein called keratin, contributing to the rigidity of the outer layer of the skin. They protect the body from the external environment, for example from stimulation, friction and pathogenic external factors, while retaining moisture.
Melanocytes: Melanocytes are found in the skin and their role is to produce and transport melanin, one of the main skin pigments that absorb light.
Fibroblasts: Fibroblasts are long, narrow cells found in the skin. They produce collagen and elastin fibers which are the main building blocks of the skin.
Erythrocytes: Erythrocytes (or red blood cells) are the carriers of hemoglobin, which also acts as a pigment by absorbing light that hits the skin.
Fat cells: They can accumulate fat and their size varies depending on the volume of fat they contain.












 Labdisc
Labdisc Botzees
Botzees Edison
Edison Telepresence Robot
Telepresence Robot DOBOT
DOBOT Keyestudio
Keyestudio Fischertechnik
Fischertechnik