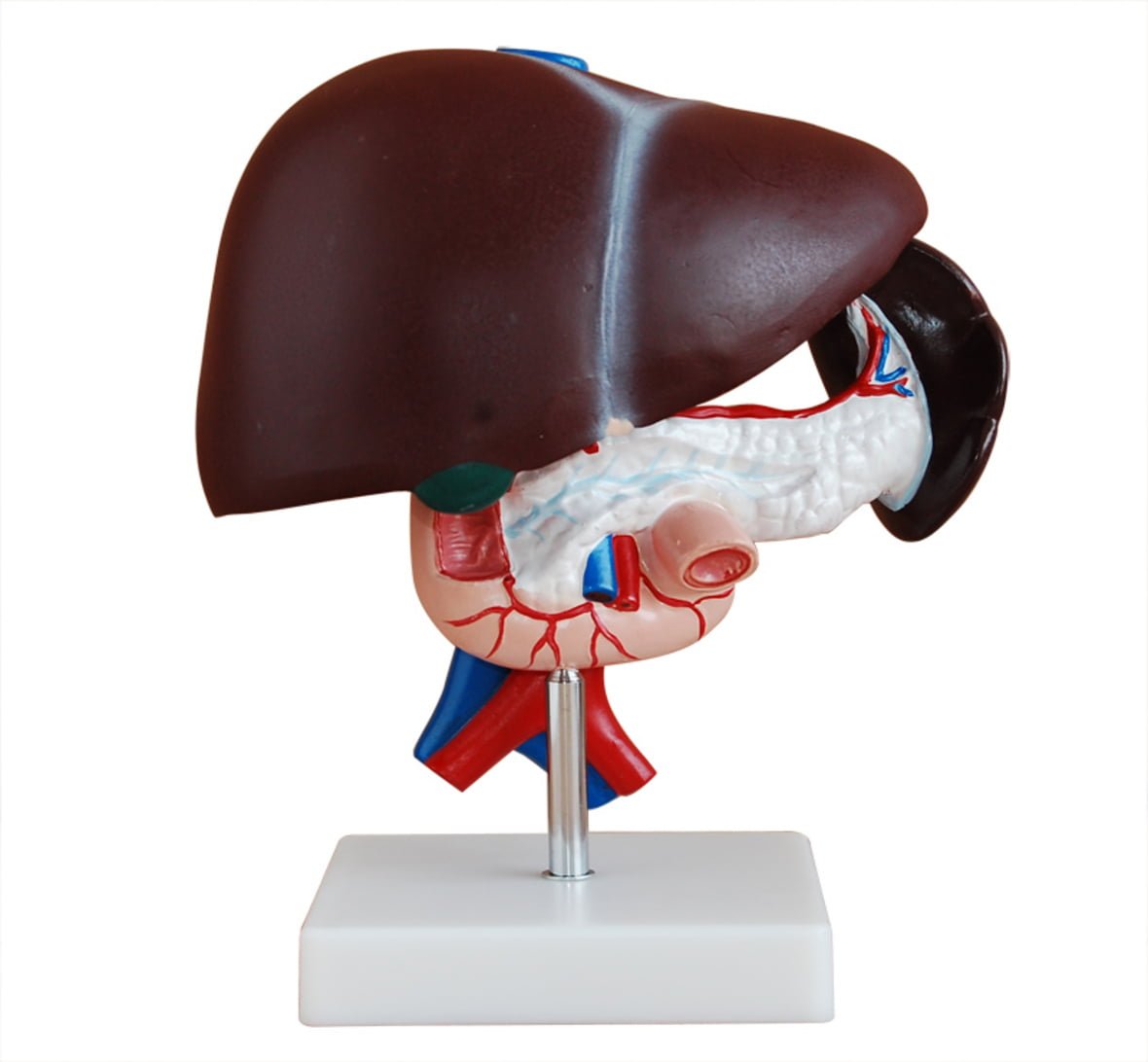
Liver Pancreas and Duodenum Model
Liver Pancreas and Duodenum Model
This model demonstrates the liver, spleen, blood vessels and pancreas. External structures are illustrated as well as the pancreatic duct of the pancreas. Also shows the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava. Dissectible into 3 parts.
Size: 23×12.5×26.5CM.
Material: PVC






 Labdisc
Labdisc Botzees
Botzees Edison
Edison Telepresence Robot
Telepresence Robot DOBOT
DOBOT Keyestudio
Keyestudio Fischertechnik
Fischertechnik