Electrophoresis for genetically modified flowers identification with SYBR dye
Genetic engineering can be used to modify food and flower crops to introduce favorable traits.
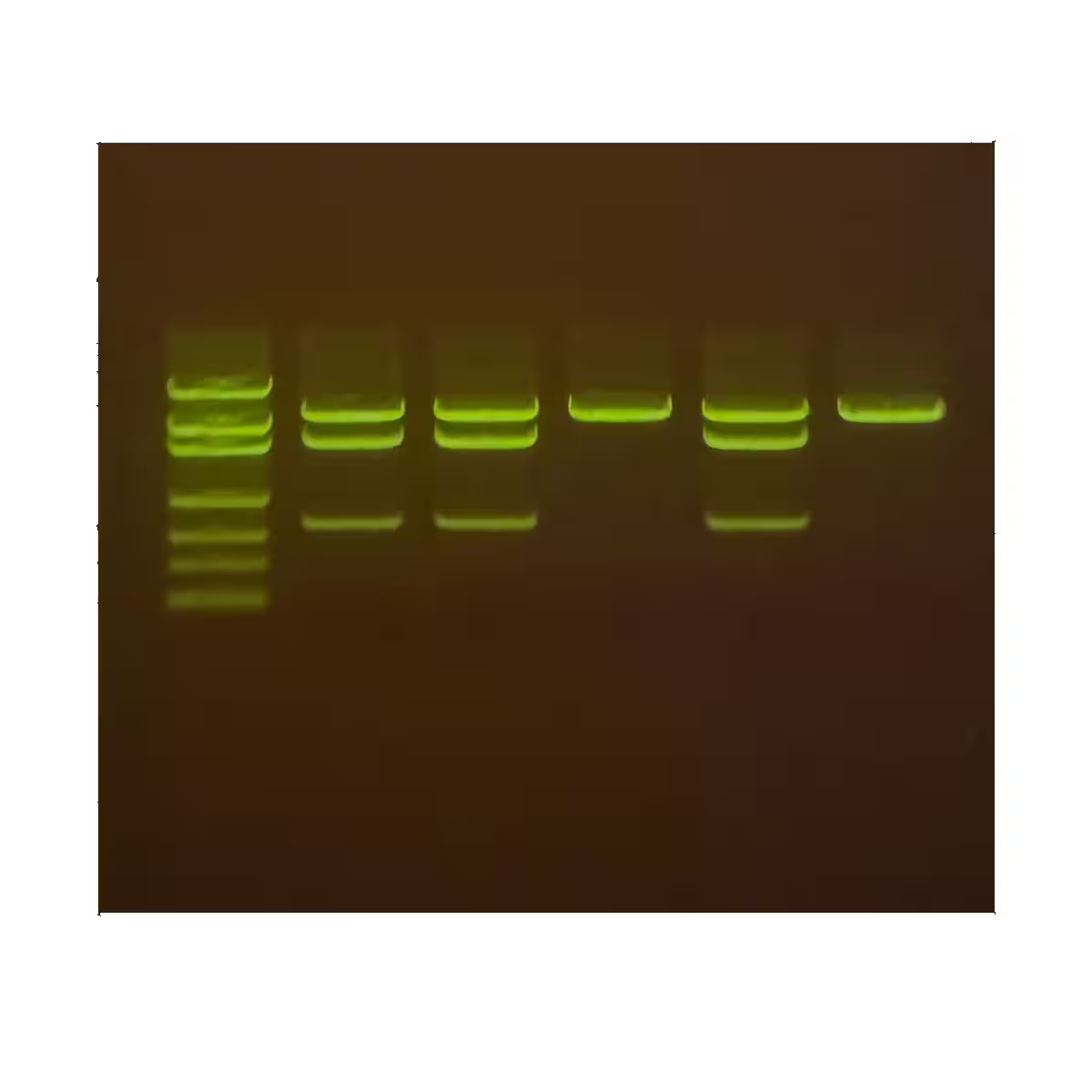
In this experiment, students will use agarose gel electrophoresis to differentiate between genetically engineered “true blue” chrysanthemums vs. artificially-dyed flowers.
By comparing the DNA patterns, students will discover how molecular biology can be used to distinguish between the genetically modified mums and the dyed ones.
• Hands-on use of core biotech tools to detect and identify genetically modified plants in simulated samples.
• Understand how electrophoresis separates differently-sized molecules.
• Perform agarose gel electrophoresis.
• Meets NGSS HS DCI LS1.A, LS3.A, LS3.B, and ETS1.B through the discussion of the structure and function of DNA, heredity and variance of traits, and use of biotechnology to make genetic modifications.
Group Size:
For 8 Gels
Time Required:
Complete in 45 minutes
Kit Includes:
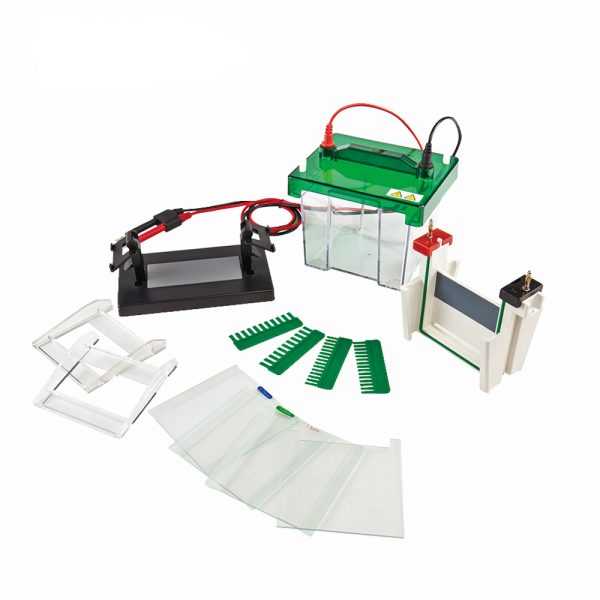
Instructions, Ready-to-Load QuickStrip™ DNA Samples, UltraSpec-Agarose™, Electrophoresis Buffer (50X), Practice Gel Loading Solution, SYBR® Safe DNA Stain.
All You Need:
DNA electrophoresis micropipetes: 5-50 µl (Optional), blue light transilluminator & Microwave or Hot Plate.
Storage:
Room Temperature Stable. Storage of Ready-to-Load QuickStrip™ samples in the Refrigerator is Recommended.






















 Labdisc
Labdisc Botzees
Botzees Edison
Edison Telepresence Robot
Telepresence Robot DOBOT
DOBOT Keyestudio
Keyestudio Fischertechnik
Fischertechnik