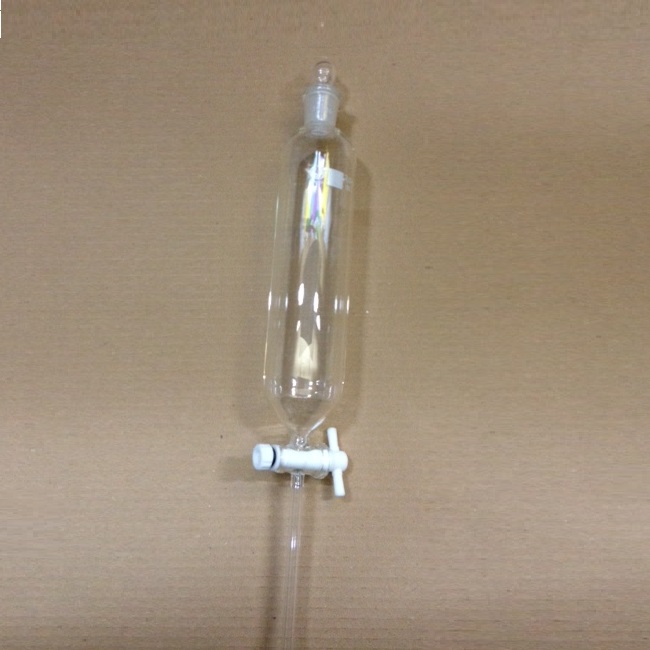
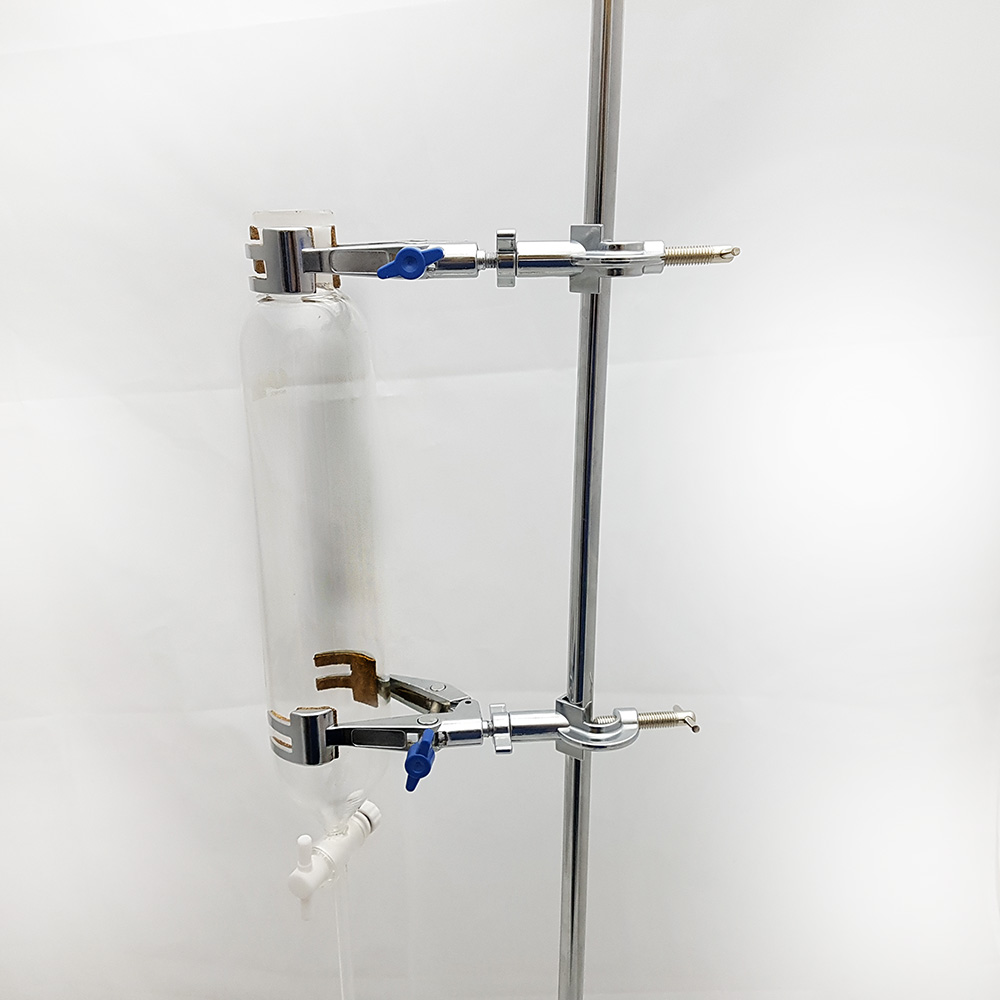
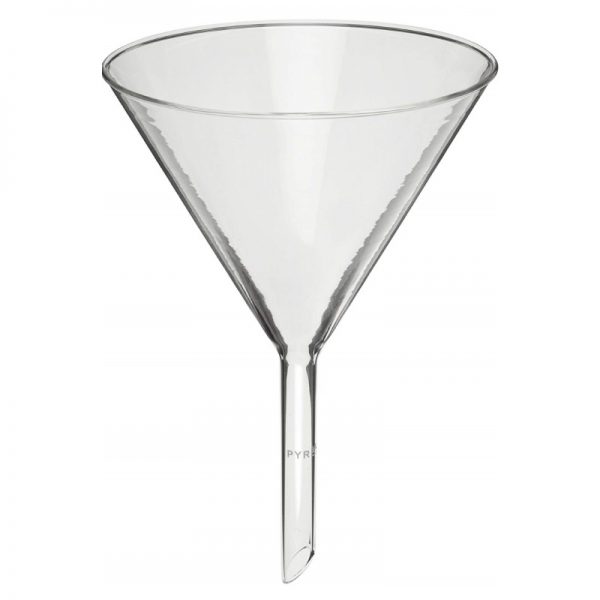
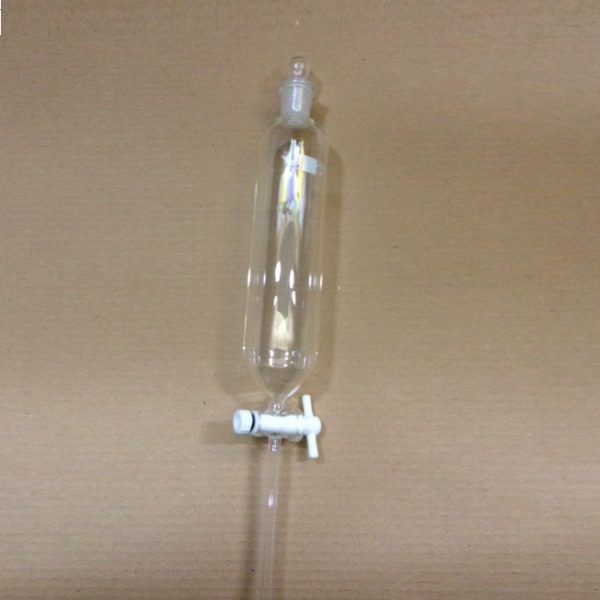
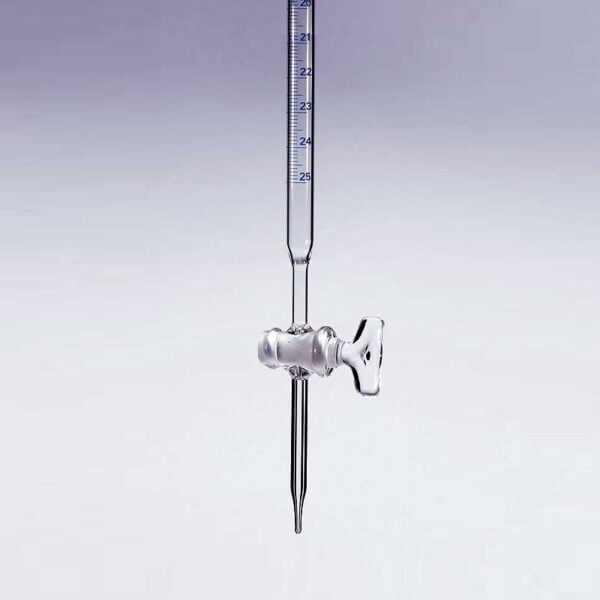
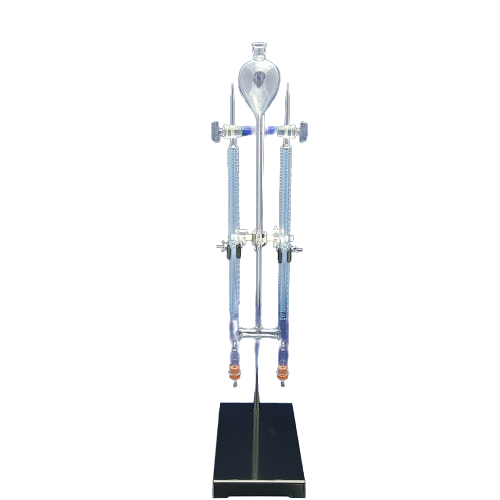
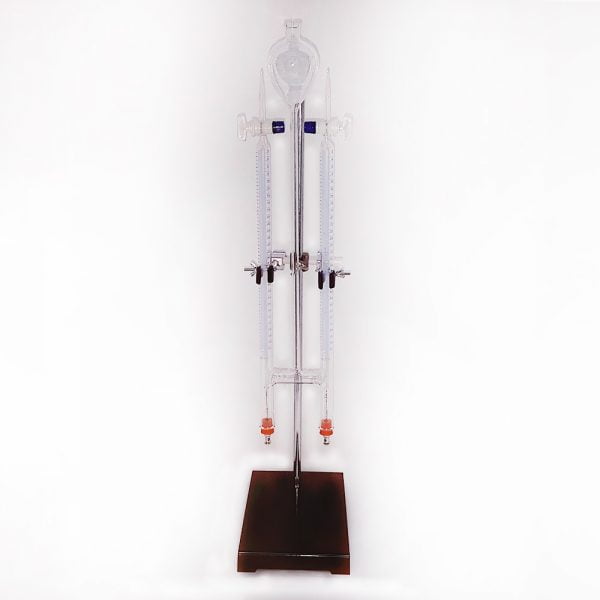
Separating funnel cylindrical teflon
Separating funnel cylindrical teflon, with stopcock
The Separating Funnel is a chemistry laboratory utensil used to separate liquids of different densities. It is an opioid drip funnel whose stenosis includes a valve. By opening the valve, the heavier liquid is allowed to flow downwards, remaining the lightest in the hopper. An example of a mixture that can be separated in a separating bottle is the water-oil mixture.
Διαθέσιμη σε:
- 125ml
- 250ml
- 500ml


 Botzees
Botzees Keyestudio
Keyestudio Fischertechnik
Fischertechnik